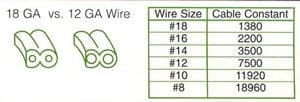
Always start your calculations with 12-gauge wire. The voltage at a fixture is the actual voltage supplied (12 Volts) minus the voltage drop. The voltage supplied may be increased by use of a multi-tap transformer. These multi-taps have alternate voltage sources to counteract a long cable run with too high of a voltage drop. Another way to counteract a high voltage drop is change to a thicker wire, such as 10-guage. If you need more voltage drop than you are getting, you may change to a thinner wire, such as 14-gauge, but a thinner wire supports less wattage.
Here is a chart to determine the maximum wattage allowed for each buried wire.
| Gauge | #18 GA | #16 GA | #14 GA | #12 GA | #10 GA | #8 GA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Wattage | 120 W | 156 W | 180 W | 240 W | 300 W | 480 W |
In addition to landscape lighting, many other interior lighting applications that use an LED light source also use low voltage wiring to conduct power from the LED driver to the lights. These calculations are similar except amperage levels, wire sizes and run distances are much lower. Some examples of interior accent lighting with lower load calculations are undercabinet lighting, display cabinet lighting, art lighting and cove lighting fixtures. If you’re interested in learning more interior load calculations or need design advice or assistance with your lighting design plan, please let us know and we would be happy to assist you.






